Back Of Skull Anatomy Labeled
Back Of Skull Anatomy Labeled. If you'd like to customize what appears on the front and back of a card, you. Bone that forms the back of the nose (behind lacrimal). It is comprised of many bones, formed by intramembranous ossification, which are joined together by sutures (fibrous joints). When this deck is imported into the desktop program, cards will appear as the deck author has made them. The brain is connected with other anatomical structures by the nerves and blood vessels going through many foramina, and the largest foramen of the skull called the foramen magnum.
The anterior fossa is formed by the orbital plates of the frontal bone, cribriform plate of the ethmoid, and lesser wings of the sphenoid. Skull, skeletal framework of the head of vertebrates, composed of bones or cartilage, which form a unit that protects the brain and some sense organs. In this video we discuss the locations of the bones of the skull and label them. The most important anatomic structures below the anterior cranial fossa are the orbits and the paranasal sinuses. Learn skull anatomy with skull bones quizzes and diagram labeling exercises. Skull anatomy gross anatomy brain anatomy medical anatomy anatomy study physician assistant education al dente. Start studying anatomy skull labels.

All the bones of skull, joined together by sutures… the skull is subdivided into 2 parts:
Anatomy and physiology7.2 the skull. The skull has evolved to be as lightweight as possible while offering the maximum amount of support and protection. The most important anatomic structures below the anterior cranial fossa are the orbits and the paranasal sinuses. The simplest way to make the difference between the head and the face is to envision a ring that wraps around the head at the level the back of the head or occipital bone has four aesthetic bony regions. The skull is a bony structure that supports the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. It is comprised of many bones, formed by intramembranous ossification, which are joined together by sutures (fibrous joints). The skull includes the upper jaw and the cranium. Learn about the anatomy of the skull bones and sutures as seen on ct images of the brain. Anatomy next provides anatomy learning tools for students and teachers. When this deck is imported into the desktop program, cards will appear as the deck author has made them. The skull begins to form prior to week 12 of embryogenesis.
Examine the cranial bones of the articulated human skull and the sectioned skull. Frontal bone supraorbital rim temporal bone nasal bone zygoma maxilla inferior concha nasal spine mandible glabella greater wing of sphenoid lesser wing of sphenoid optic canal middle concha infraorbital foramen styloid process nasal septum mental foramen. The greater portion of the anterior floor is convex inferior relationships — extracranial aspects. Overview, anterior skull base, middle skull base march 18, 2017. Axial muscles of the head, neck, and back. We also cover the ear bones and the hyoid bone.transcript/notesskull. It offers protection to the brain, eye balls, inner ears, and nasal passages. In this video we discuss the locations of the bones of the skull and label them.

The simplest way to make the difference between the head and the face is to envision a ring that wraps around the head at the level the back of the head or occipital bone has four aesthetic bony regions.
Looking at it from the inside it can be learn everything about the bones of the skull with our articles, video tutorials, labeled diagrams, and quizzes. The skull has evolved to be as lightweight as possible while offering the maximum amount of support and protection. Overview, anterior skull base, middle skull base march 18, 2017. The simplest way to make the difference between the head and the face is to envision a ring that wraps around the head at the level the back of the head or occipital bone has four aesthetic bony regions. Skull, skeletal framework of the head of vertebrates, composed of bones or cartilage, which form a unit that protects the brain and some sense organs. The anterior fossa is formed by the orbital plates of the frontal bone, cribriform plate of the ethmoid, and lesser wings of the sphenoid. Anatomical structures of the skull include: As a review activity, label figures 13.1, 13.2, 13 3, 13.4, and 13.5. Review a textbook section on the skull. A cartilaginous mould begins to grow this is why raising your eyebrows can create the appearance that the back of the head is moving. We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. Axial muscles of the head, neck, and back. William is a final year medical student in australia who has taught anatomy to tertiary science and. Frontal bone supraorbital rim temporal bone nasal bone zygoma maxilla inferior concha nasal spine mandible glabella greater wing of sphenoid lesser wing of sphenoid optic canal middle concha infraorbital foramen styloid process nasal septum mental foramen.
Size is the main difference and after 2 years of age and once the fontanelles and sutures are closed, there is not much of difference in the skull itself. It offers protection to the brain, eye balls, inner ears, and nasal passages. The greater portion of the anterior floor is convex inferior relationships — extracranial aspects. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. Skull, skeletal framework of the head of vertebrates, composed of bones or cartilage, which form a unit that protects the brain and some sense organs. The skull begins to form prior to week 12 of embryogenesis. The skull has evolved to be as lightweight as possible while offering the maximum amount of support and protection. Anatomical structures of the skull include: Axial muscles of the head, neck, and back.
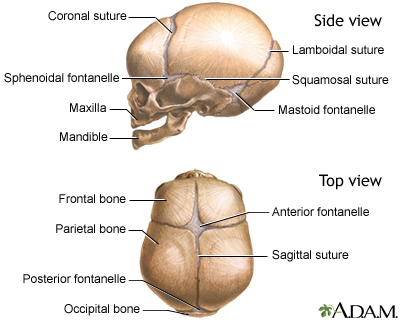
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website.
Overview, anterior skull base, middle skull base march 18, 2017. Excluding ear ossicles, it is made of 22 bones. That is how the doctor insights on: Frontal bone supraorbital rim temporal bone nasal bone zygoma maxilla inferior concha nasal spine mandible glabella greater wing of sphenoid lesser wing of sphenoid optic canal middle concha infraorbital foramen styloid process nasal septum mental foramen. When this deck is imported into the desktop program, cards will appear as the deck author has made them. It offers protection to the brain, eye balls, inner ears, and nasal passages. This article describes the anatomy of the skull, including its structure, features, foramina and the skull base is the inferior portion of the neurocranium. A cartilaginous mould begins to grow this is why raising your eyebrows can create the appearance that the back of the head is moving. Anatomy next provides anatomy learning tools for students and teachers. This anatomic region is complex and poses surgical challenges for otolaryngologists and neurosurgeons alike. The brain is connected with other anatomical structures by the nerves and blood vessels going through many foramina, and the largest foramen of the skull called the foramen magnum. Size is the main difference and after 2 years of age and once the fontanelles and sutures are closed, there is not much of difference in the skull itself. Labelled poster sized anatomical illustration of the bones of the skull in anterior view available to license on a rights managed basis.
Size is the main difference and after 2 years of age and once the fontanelles and sutures are closed, there is not much of difference in the skull itself back of skull anatomy. The skull is a bony structure that supports the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain.
Posting Komentar untuk "Back Of Skull Anatomy Labeled"